R2 Bucket Setup
In this section, you'll create your first Cloudflare R2 bucket and configure it for your note-taking application. You'll learn how to connect your bucket to your Worker and set up proper security with CORS policies.
Understanding R2 Object Storage
What is R2? Cloudflare R2 is a cloud storage service that lets you store files like images, documents, and videos. Think of it as a giant digital filing cabinet that your application can access from anywhere in the world.
Why Use R2?
- Zero egress fees - No charges for downloading files
- S3 Compatible - Works with existing S3 tools and libraries
- Global distribution - Files are stored close to your users
- Secure - Built-in security features and access controls
Key Concepts:
- Bucket - A container that holds your files (like a folder)
- Object - The actual file you store (image, document, etc.)
- Key - The unique name/path for each file in the bucket
- Binding - Connects your Worker code to your R2 bucket

Prerequisites
Before starting, ensure you have completed Module 2, which includes:
- Database Setup - D1 database configured
- CRUD Implementation - API endpoints working
- Deployment Configuration - Backend deployed
- Currently in
blazenote-backendproject directory
Verify Your Setup
# Navigate to your backend project
cd ~/projects/blazenote-backend
# Verify you're logged in to Cloudflare
wrangler whoami
# Should show your Cloudflare email
# Check current project status
git status
# Should show clean working directory
Step 1: Create Your R2 Bucket
Understanding Buckets
What is a bucket? A bucket is like a main folder where all your files will be stored. Each bucket has a unique name and can hold unlimited files.
Create the Bucket
Run the bucket creation command:
wrangler r2 bucket create blazenote
What this command does:
- Creates a new R2 bucket named "blazenote" in your Cloudflare account
- Sets up the bucket in Cloudflare's global network
- Prepares the bucket to store your application's files
Expected output:
Created bucket 'blazenote' with default storage class set to Standard.
Verify Bucket Creation
Check that your bucket was created:
wrangler r2 bucket list
Expected output:
blazenote
Alternative verification:
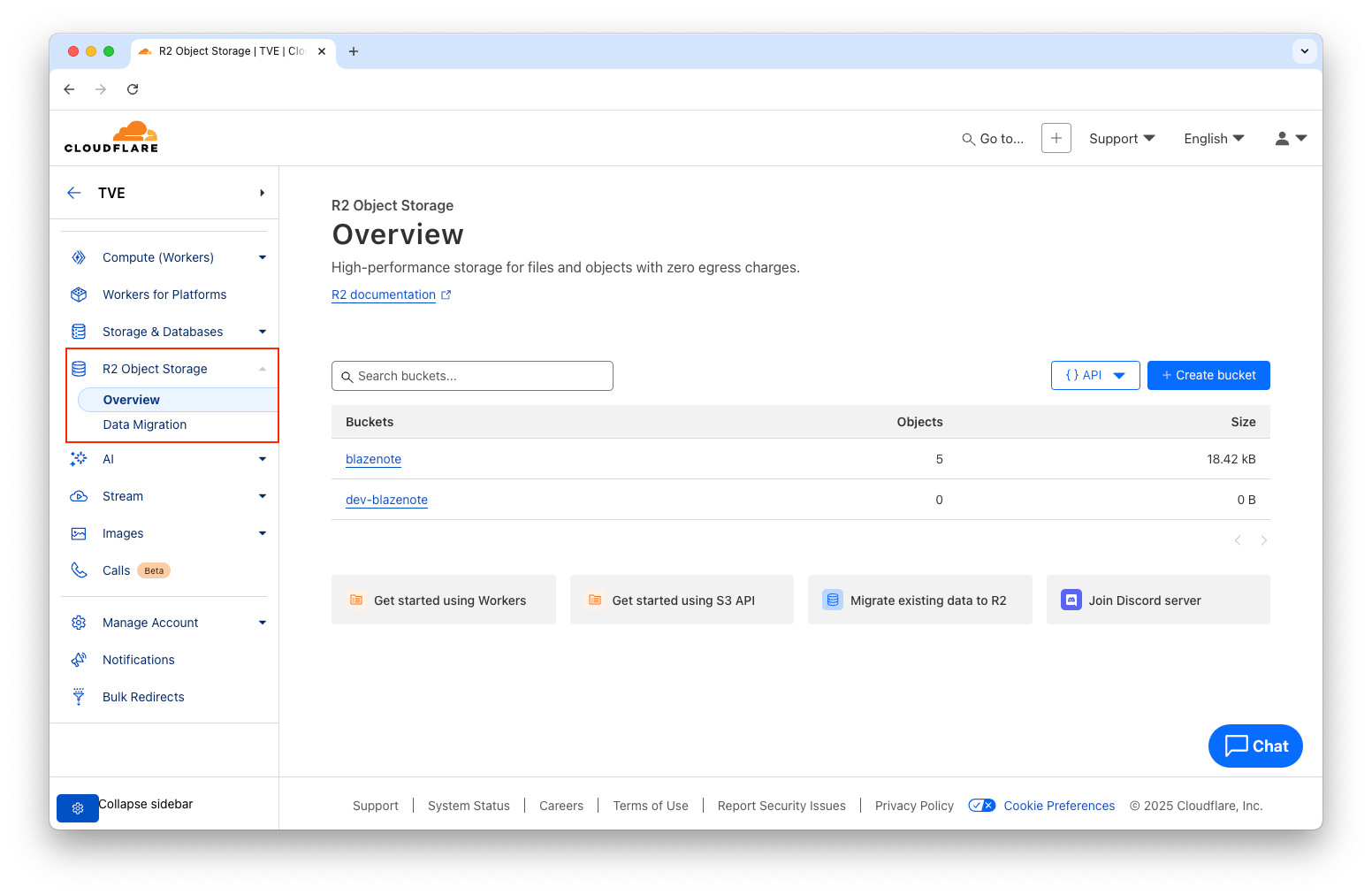
- Go to Cloudflare Dashboard
- Navigate to R2 Object Storage
- You should see your
blazenotebucket listed
Step 2: Connect Your Bucket to Your Worker
Understanding Worker Bindings
What is a binding? A binding connects your Worker (backend code) to your R2 bucket, allowing your code to upload, download, and manage files.
Update Configuration File
Open your wrangler.toml file:
code wrangler.toml
Find the R2 section and uncomment it:
# Find this section (it should be commented out):
# [[r2_buckets]]
# binding = "R2_BUCKET"
# bucket_name = "blazenote"
# preview_bucket_name = "dev-blazenote"
# Uncomment it to look like this:
[[r2_buckets]]
binding = "R2_BUCKET"
bucket_name = "blazenote"
preview_bucket_name = "dev-blazenote"
What this configuration does:
binding = "R2_BUCKET"- Creates a variable calledR2_BUCKETin your codebucket_name = "blazenote"- Points to your production bucketpreview_bucket_name = "dev-blazenote"- Uses a separate bucket for testing
Step 3: Set Up Security with CORS
Understanding CORS for File Storage
What is CORS? CORS (Cross-Origin Resource Sharing) is a security feature that controls which websites can access your files. Without proper CORS setup, your frontend won't be able to upload or download files.
Configure CORS Policy
Go to your Cloudflare Dashboard:
- Navigate to R2 Object Storage
- Click on your
blazenotebucket - Go to the Settings tab
- Click Add CORS Policy
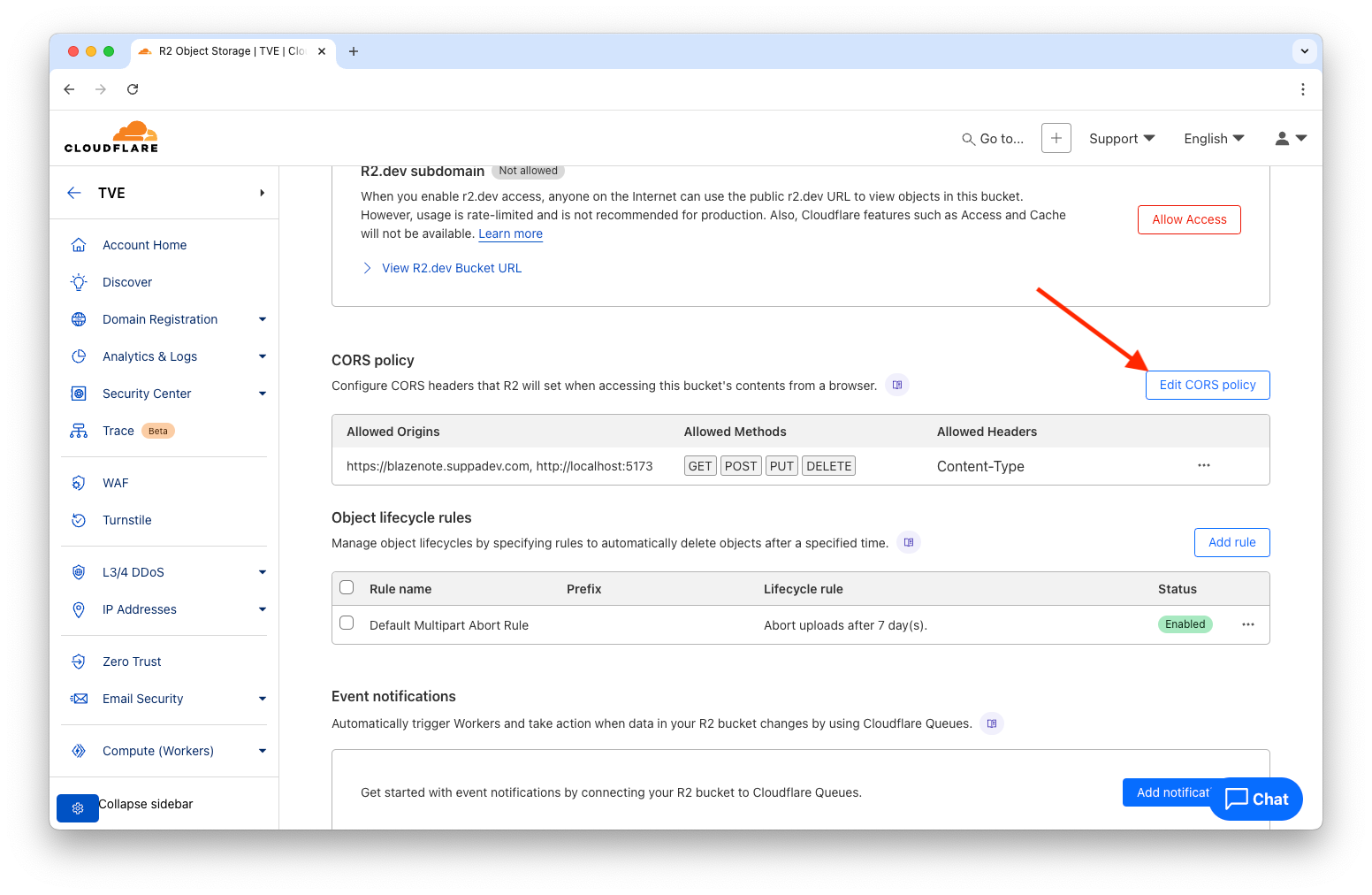
Add this CORS policy:
[
{
"AllowedOrigins": [
"https://your-frontend-domain.com",
"http://localhost:5173"
],
"AllowedMethods": ["GET", "POST", "PUT", "DELETE"],
"AllowedHeaders": ["Content-Type"]
}
]
⚠️ Important: Replace https://your-frontend-domain with your actual frontend domain from Module 1. For example: https://blazehack-frontend.earthy-captain.sxptest.com
What this policy does:
- AllowedOrigins - Only these websites can access your files
- AllowedMethods - What actions are allowed (upload, download, delete)
- AllowedHeaders - What information can be sent with requests